
Unlocking the Mysteries of Cellular Diffusion | Cambridge IGCSE Biology
Watch the Video at the End of This Blog to Unlock the Mysteries of Cellular Diffusion ↓
This article explains diffusion and how it occurs. We’ll also cover Brownian motion.
What is Diffusion?
Diffusion is the net movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration down a concentration gradient as a result of their random movement.
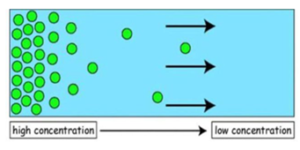
In the diagram above, the blue rectangle represents space, and the green circles represent particles. The particles are concentrated at one end, while the other end is empty.
Diffusion is the natural tendency of particles to spread from a region of high concentration to a region of lower concentration.
What does “net movement of molecules” mean?
Molecules move randomly, not along a fixed path. Although each particle moves randomly, when we observe all particles together, the net movement is from higher to lower concentration. This is why we use the term “net movement.”
What does “down a concentration gradient” mean?
In the diagram, the left region has many particles (higher concentration), while the right has fewer (lower concentration). This difference is the concentration gradient.
Since particles move from higher to lower concentration, we say they move down the concentration gradient as a result of random movement.
Key terms for the definition:
- Movement of particles
- Higher concentration
- To lower concentration
- Down a concentration gradient
- Random movement
This is the definition of diffusion you need to write if asked in the exam.
Why is Diffusion Important in Biology?
Diffusion occurs across every cell in our body. We know that cells contain a nucleus, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. Multicellular organisms, like humans, have billions of cells. Diffusion takes place in almost every one of these cells.
Why does diffusion need to take place in our cells?
Absorbing useful substances:
Imagine a useful substance outside the cell at high concentration, while inside the cell it’s at low concentration. By diffusion, these particles move from high to low concentration, so more useful substances enter the cell.
Removing waste products:
If the cell has produced waste products at high concentration inside, and outside there’s a lower concentration, diffusion moves these waste substances out of the cell.
This is how diffusion applies in living organisms: some substances move into cells and some move out through the cell membrane by diffusion.
What is the Driving Force Behind Diffusion?
Where do particles get the energy to diffuse?
The energy comes from the kinetic energy of random movement of molecules and ions. Molecules and ions are in constant random motion, known as Brownian motion.
Brownian motion is the random motion shown by molecules and ions, and this random motion is a result of the kinetic energy of particles.
All particles contain kinetic energy, which drives their random motion. As particles move randomly, they collide with each other and with container walls, causing them to spread out and move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration.
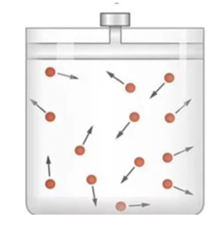
Kinetic energy is directly related to temperature. If the temperature increases, kinetic energy increases. Particles with greater energy show higher rates of random movement, and therefore, higher rates of diffusion.
Need help mastering IGCSE Biology concepts?
Book a Free SessionRevising: Unlocking the Mysteries of Cellular Diffusion
Diffusion is one of the most important processes by which substances move in and out of cells. Make sure you study the full definition, as it’s a frequent exam question.
Some questions on movement into and out of cells can be found here. You can time your answers to see if you can complete the quiz within the time limit.
If you’re struggling with IGCSE revision or Biology in particular, you can reach out to us at Tutopiya to join revision sessions or find the right tutor for you.
Attempt the quiz to know where you stand!
Watch: Unlocking the Mysteries of Cellular Diffusion
About the author
Kulni Gamage is a contributing writer who breaks down complex biology concepts for IGCSE students. She focuses on clear explanations, visual aids, and practical exam strategies to help students master challenging topics.
Ready to Excel in Your Studies?
Get personalised help from Tutopiya's expert tutors. Whether it's IGCSE, IB, A-Levels, or any other curriculum — we match you with the perfect tutor and your first session is free.
Book Your Free TrialWritten by
Kulni Gamage
Contributing Writer
Related Articles

IGCSE Additional Mathematics Revision Notes, Syllabus, Benefits and Study Resources
Discover IGCSE Additional Mathematics through Tutopiya's learning platform. Get expert guidance, revision notes, and study resources to excel in your exams.

IGCSE Economics: Mindmaps + Revision Notes for Download!
Download IGCSE Economics mindmaps and revision notes to ace your exams. Get comprehensive resources for quick and effective study.

Top 10 Secrets to Ace IGCSE Exams with Online Tuition
Unlock the top 10 secrets to ace IGCSE exams with Tutopiya's online tuition. Personalized learning plans, expert tutors, and tools for success.
