
IGCSE Economics: Mindmaps + Revision Notes for Download!
When you’re preparing for Cambridge IGCSE Economics, remember that the qualification is globally recognised as solid preparation for further study—which means your revision strategy needs to be just as rigorous. Strong notes, clear mindmaps, and consistent past-paper practice make the difference between a pass and a top score.
“IGCSE Economics requires you to pass an exam to demonstrate your proficiency.”
Tips Before the IGCSE Economics Exam
Before sitting the IGCSE Economics exam, review the assessment objectives:
- Knowledge with understanding
- Analysis
- Judgement and decision-making
- Critical evaluation
Next, revisit the syllabus content. Make sure you can:
- Define basic economic problems and allocation of resources
- Describe the roles of producers, consumers, and borrowers
- Explain the role of government in an economy
- Interpret key economic indicators
- Discuss why nations are classified as developing economies
In order to keep definitions fresh, use mindmaps and flashcards. We’ve prepared downloadable resources to help you revise faster.
Download the Full Notes Pack

Ace your IGCSE Economics exams. Access detailed mindmaps and revision notes today: Download Tutopiya Economics Notes (PDF)
Need structured IGCSE Economics revision sessions?
Book a Free SessionIGCSE Economics Notes Overview
Demand and Supply
Market prices depend on demand and supply. Both fluctuate constantly and directly affect business performance.
- Market: any place buyers and sellers meet to trade products
- Demand: quantity customers are prepared to buy at different prices
- Supply: quantity firms are prepared to sell at different prices
There are many market types (goods, commodities, labour). Successful advertising boosts demand and usually increases price; new entrants boost supply and can lower price.
Business Cycle
The business cycle tracks expansion and contraction over time, usually via real GDP. Four stages:
- Growth – rising GDP, falling unemployment, higher profits
- Boom – excess spending, rising inflation, costly factors of production
- Recession – falling GDP, lower demand
- Slump – high unemployment, business closures
Economic Growth
Economic growth is the increase in goods and services produced per head over time. Sustained growth raises living standards but may create environmental or distributional challenges.
Market Failure
Market failure occurs when resources are misallocated, leading to overproduction, underproduction, or missing markets. Examples include negative externalities and public goods.
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply
- Aggregate demand: total spending on goods and services at a given price level
- Aggregate supply: total output firms will produce at a given price level
AD and AS together determine national income, price levels, and long-run growth potential.
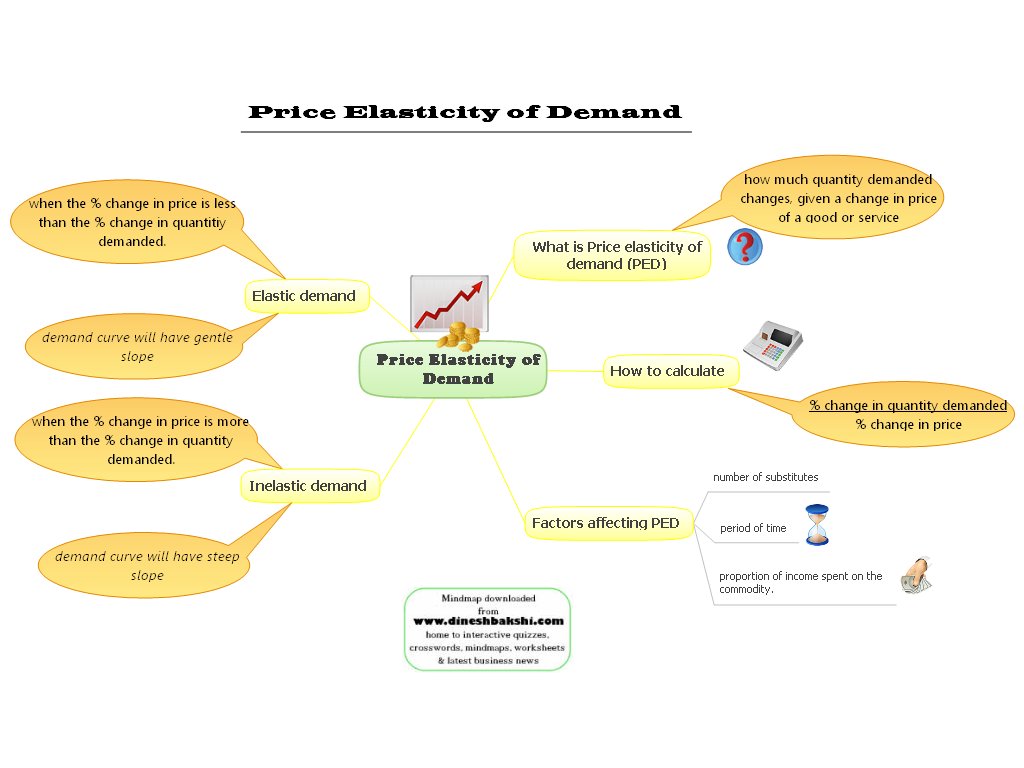
Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Price Elasticity of Demand measures how responsive demand is to price changes.
- Elastic demand (|PED| > 1): consumers respond strongly to price changes
- Inelastic demand (|PED| < 1): consumers are less responsive
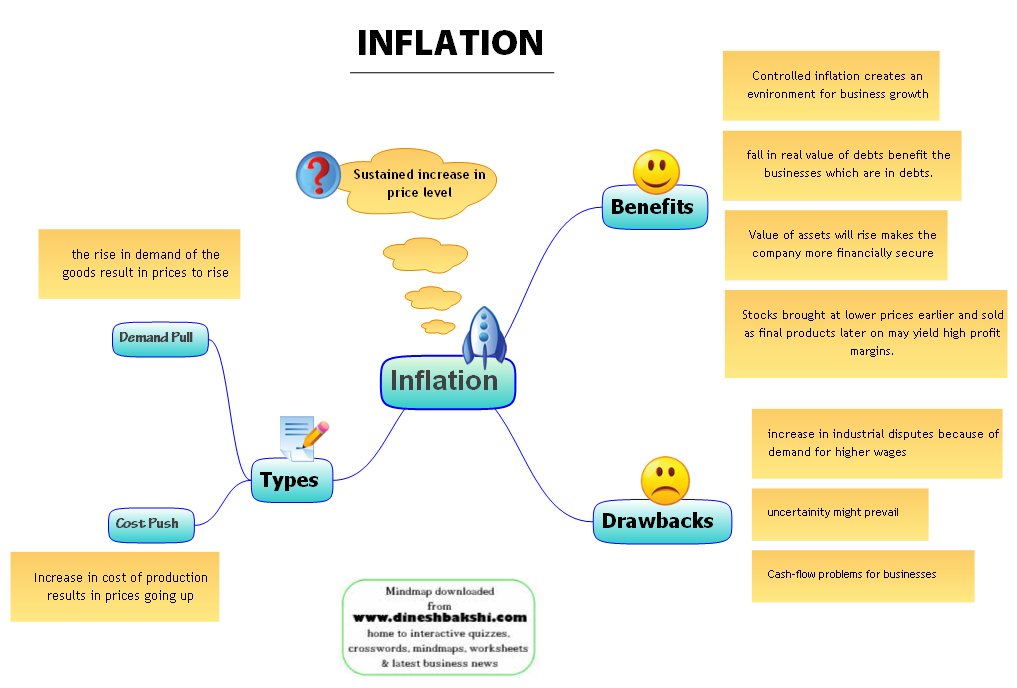
Inflation
Inflation impacts housing, food, healthcare, transport, and more. Understand the causes (demand-pull, cost-push) and consequences (loss of purchasing power, menu costs, uncertainty).
Quick-Access Resources
Boost your IGCSE Economics prep with live tutoring
Access Learning PlatformAbout the author
Nuha Gouse is the co-founder of Tutopiya and a first-class honours Math graduate from Imperial College London. She is passionate about delivering personalised, high-quality online tutoring that helps students learn at their own pace and build exam confidence.
Ready to Excel in Your Studies?
Get personalised help from Tutopiya's expert tutors. Whether it's IGCSE, IB, A-Levels, or any other curriculum — we match you with the perfect tutor and your first session is free.
Book Your Free TrialWritten by
Nuha Ghouse
Co-founder
Related Articles

IGCSE Additional Mathematics Revision Notes, Syllabus, Benefits and Study Resources
Discover IGCSE Additional Mathematics through Tutopiya's learning platform. Get expert guidance, revision notes, and study resources to excel in your exams.

Top 10 Secrets to Ace IGCSE Exams with Online Tuition
Unlock the top 10 secrets to ace IGCSE exams with Tutopiya's online tuition. Personalized learning plans, expert tutors, and tools for success.
IGCSE Exam Success: How Mock Exams Help Reduce Stress
Learn how mock exams reduce stress and boost performance for IGCSE students. Get tips to ace your exams confidently.
