- Download IGCSE Economics mindmaps and revision notes to ace your exams. Get comprehensive resources for quick and effective study.
When you’re preparing to sit for the IGCSE Economics exam, it is important to first note the importance of this international qualification. Institutions throughout the world recognize this qualification as the best preparation a student would face before their university-level study and good IGCSE Economics notes certainly help.
“IGCSE Economics requires you to pass an exam to demonstrate your proficiency.”
To obtain a good score requires diligent study practices and constant revision of past paper materials.
Tips before the IGCSE Economics exam
Before sitting for the IGCSE Economics exam, it is important for you to review the assessment requirements for the exam, such as knowledge with understanding, analysis, judgement and decision-making and critical evaluation.
You must be able to cover all four objectives in the context of economics. Once you’ve covered all objectives, you are required to go through all its content in the curriculum.
You must be able to define basic economic problems, understand the allocation of resources, describe the functions of a producer, consumer and borrower in an economy, describe the role of the government in an economy, explain economic indicators and state the reasons some countries are classified as developing economies.
In order for you to remember all economic definitions, we have noted all economic definition mind maps for you to understand the concept a lot better and faster!
You can also download our very own Economic notes for revision here!
Ace your IGCSE Economics exams. Access detailed mindmaps and revision notes today Download Here
IGCSE Economics notes
To start with the most essential and basic IGCSE Economics notes, let us consider the market price.
Demand and Supply
Market prices depend on the levels of demand and supply. These levels rise and fall according to a number of factors, and can have a big impact on the success of a business.
A market is any place where buyers and sellers meet to trade products. The market price is the amount customers are charged for each item which depends on the demand and supply.
Demand is the number of product customers is prepared to buy at different prices.
Supply is the amount of a product businesses are prepared to sell at different prices.
There are many different types of markets. The goods market is where everyday products such as DVDs are traded.
The commodities market is where raw materials such as wheat are traded.
“Market prices change when supply and demand patterns change.”
– An increase in demand following a successful advertising campaign usually causes an increase in price.
– An increase in supply when a new business opens usually causes a fall in price.
Business Cycle
Business Cycle is a series of cycles of economic expansion and contraction.
The cycle involves shifts over time between periods of the relatively rapid growth of output and periods of relative stagnation or decline.
These fluctuations are often measured using the real gross domestic product.
4 stages of a business cycle
There are four main stages in a business cycle:
Growth – Where GDP rises, unemployment falls and business experience rising profits.
Boom – Results of excess spending, economy experience rapid inflation and factors of production becomes expensive.
Recession – Results from lack of spending, GDP is falling and demand in the economy falls.
Slump – High levels of unemployment and business rapidly close down.
Economic Growth
Economic Growth an increase in the number of goods and services produced per head of the population over a period of time.
Market Failure
Market Failure – Inefficient distribution of goods and services in the free market.
Aggregate Demand and Supply
Aggregate demand – is an economic measurement of the sum of all final goods and services produced in an economy, expressed as the total amount of money exchanged for those goods and services.
Since aggregate demand is measured by market values, it only represents total output at a given price level. It does not necessarily represent the quality or standard living.
Aggregate supply – also known as total output is the total supply of goods and services produced within an economy at a given overall price level in a given period.
It is represented by the aggregate supply curve, which describes the relationship between price levels and the quantity of output that firms are willing to provide.
Normally, there is a positive relationship between aggregate supply and the price level.
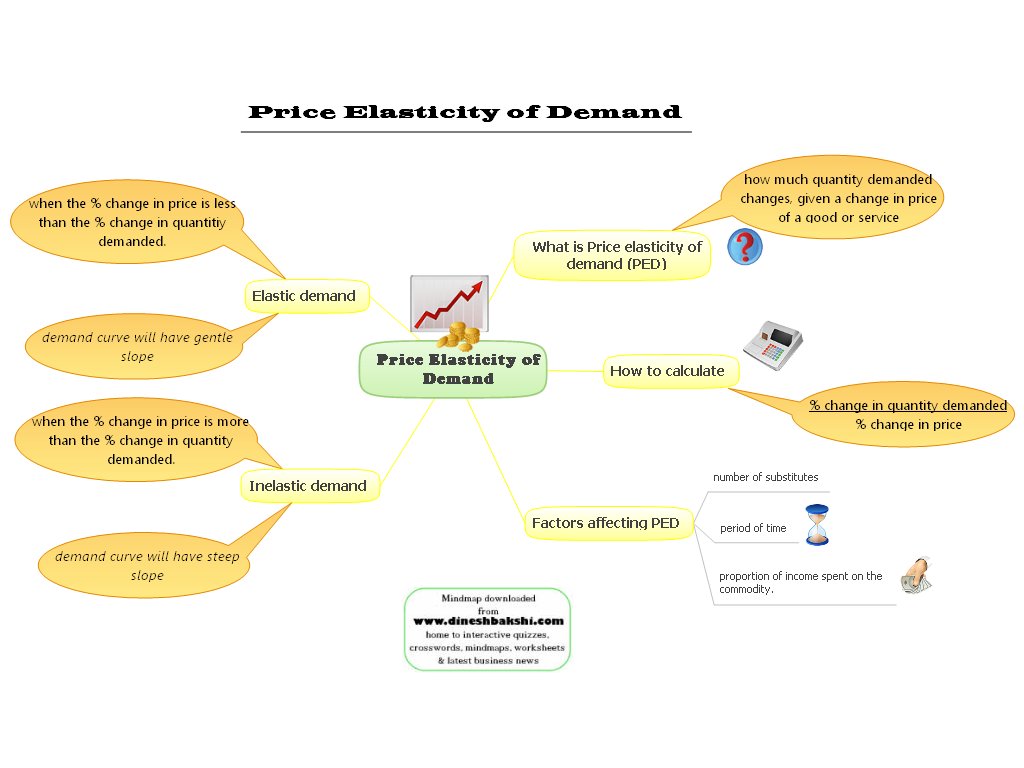
Price of Elasticity of Demand
Price Elasticity of Demand – measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in products own price.
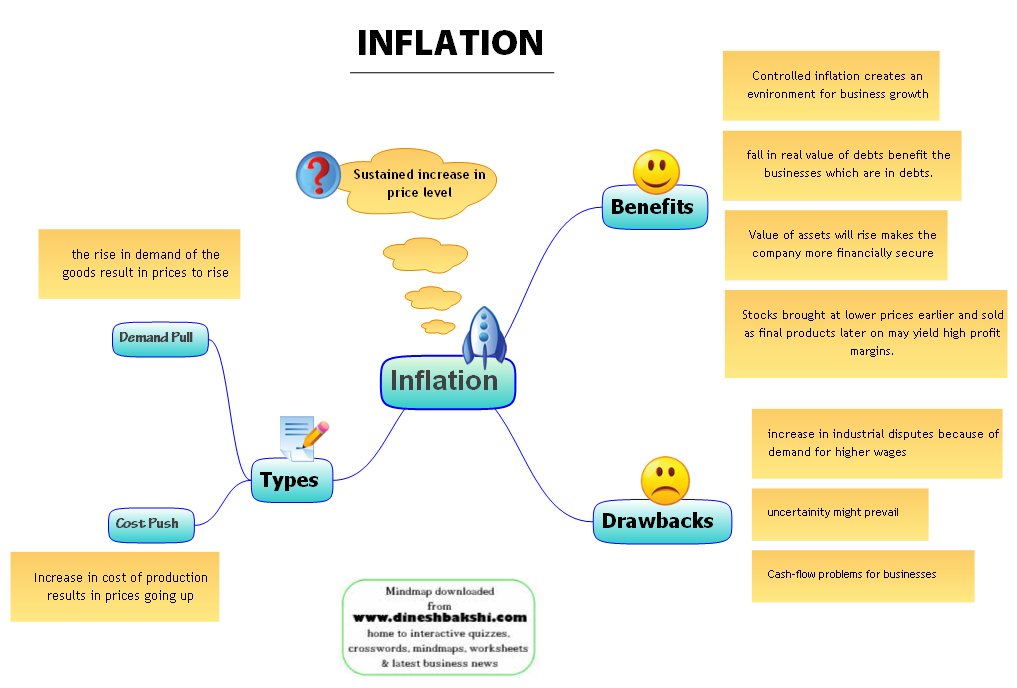
Inflation
Inflation affects everything around us, from basic necessities like housing, food, medical care and utilities to the cost of cosmetics, and new automobiles.
Download our IGCSE Economics notes here!
Boost your IGCSE Economics prep. Download mindmaps and notes now Get Your Notes
Nuha Ghouse
Nuha Gouse is the Co-founder of Tutopiya and is equipped with a first class honours Math degree from Imperial College, London. Her mission is to provide personalized individual lessons online where students from around the world can learn at their own pace and convenience.




